Spring boot提供了默认的异常处理机制,但是难以满足业务需要,一般需要编码来实现自己的业务处理机制。在本篇,将介绍如何自定义异常页面,和进行全局的异常处理。
1. 全局异常处理
如果系统业务处理发生异常,我们希望能够将异常信息以友好的形式返回给调用方,而不是仅在后台记录日志,尤其是在开发RESTFul的API时,需要将业务异常信息进行明确定义并返回给API调用方,这显得尤为重要。
现在,我们来定义一个全局的业务异常类BusinessException,如果业务处理失败抛出该类或者其子类,然后编写一个全局异常处理器,将异常转换为有好的信息并返回。
1、定义异常类
public class BusinessException extends Exception {
public BusinessException() {
super();
}
public BusinessException(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
public BusinessException(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}
public BusinessException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public BusinessException(MsgDefinition msgDefinition) {
super(msgDefinition.msgOf());
this.msgDef = msgDefinition;
}
public MsgDefinition msgDef() {
return msgDef == null ? MsgDefinition.UNKOWN_ERROR : msgDef;
}
}其中的MsgDefinition为具体的错误信息,包含错误码code和错误提示信息msg,子类继承该类进行扩展:
public class MsgDefinition {
public static final MsgDefinition SUCCESS = new MsgDefinition("0000", "请求成功");
public static final MsgDefinition EMPTY_ARGUMENTS = new MsgDefinition("4001", "请求参数为空");
public static final MsgDefinition ILLEGAL_ARGUMENTS = new MsgDefinition("4002", "请求采参数非法");
public static final MsgDefinition FILE_SIZE_OVER_LIMIT = new MsgDefinition("4301", "文件大小超过限制");
public static final MsgDefinition FILE_NUMBER_OVER_LIMIT = new MsgDefinition("4302", "文件数量超过限制");
public static final MsgDefinition FILE_FORMAT_UNSUPPORTED = new MsgDefinition("4310", "文件格式不支持");
public static final MsgDefinition UNKOWN_ERROR = new MsgDefinition("9999", "系统未知异常");
private String code;
private String msg;
public MsgDefinition(String code, String msg) {
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
}
public String codeOf() {
return this.code;
}
public String msgOf() {
return this.msg;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return JsonUtil.toJson(this);
}
}2、定义全局异常处理器
我们希望在每个Controller的每个@RequestMapping方法抛出异常时进行处理,需要使用@ControllerAdvice注解,另外,还需要使用@ExceptionHandler,它用于声明处理的异常类型,代码如下:
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(value = {BusinessException.class})
@ResponseBody
public ResultMsg jsonErrorHandler(HttpServletRequest request, BusinessException exception) {
URLResultMsg result = new URLResultMsg();
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
result.setUrl(uri);
MsgDefinition md = exception.msgDef();
if (md != null) {
String code = md.codeOf();
String msg = md.msgOf();
result.setRtnCode(code);
result.setRtnMsg(msg);
result.setType(ResultMsg.MESSAGE_TYPE_ERROR);
} else {
result.setRtnCode(MsgDefinition.UNKOWN_ERROR.codeOf());
result.setRtnMsg(exception.getMessage());
result.setType(ResultMsg.MESSAGE_TYPE_ERROR);
}
return result;
}
}jsonErrorHandle为异常处理方法, 当Controller抛出BusinessException时,会进入该方法。其逻辑很简单,通过获取BusinessException的消息定义对象,将异常转换为URLResultMsg,并返回,最终该对象会被转换为json字符串。
3、测试
编写一个Controller:
@Controller
public class HomeController {
@GetMapping("/json")
@ResponseBody
public ResultMsg json() throws Exception {
throw new BusinessException(MsgDefinition.EMPTY_ARGUMENTS);
}
}直接让其抛出BusinessException异常,启动应用,访问http://localhost:8080/json,得到结果为:
``{"rtnCode":"4001","rtnMsg":"请求参数为空","data":null,"type":"error","url":"/json"}``说明全局异常处理器生效,成功将异常转换为更友好的错误提示信息。业务上,只需要继承BusinessException异常,来定义自身更明确的异常,而不需要修改全局异常处理器。
2. 自定义异常页面
Spring Boot本身提供的错误页面非常不友好,需要自己定义,而方法有多种。
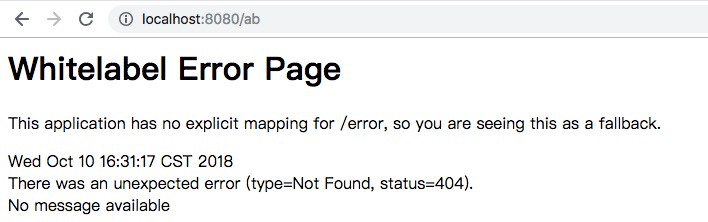
最简单有效的方式是,在工程中直接新建错误页面,Spring Boot会优先使用之。一般而言,应用会根据Http请求的错误码来决定使用哪个页面,比如常见的500、404、400、405等,Spring Boot提供了重写这些页面的方式,只需在工程的文件夹中存放新建的这些页面即可,比如404页面存放路径如下:
使用静态html:
src/
+- main/
+- java/
| + <source code>
+- resources/
+- public/
+- error/
| +- 404.html
+- <other public assets>使用模板:
src/
+- main/
+- java/
| + <source code>
+- resources/
+- templates/
+- error/
| +- 5xx.ftl
+- <other templates>注意页面名称必须与HTTP错误码相同,并且是放在error文件夹下。也可以使用模糊匹配,如上边的5xx.ftl,所有的5xx错误码都会被映射到该页面中。
另外,Spring Boot会将页面Model放入如下信息:
timestamp:错误时间戳
status:Http状态码
error:Http错误信息
message:后台定义的错误信息
path:请求的uri
我们看一个5xx页面的例子:
1、定义5xx错误页面
这里使用的是默认的Thymeleaf模板,页面位置为src/main/resources/templates/error/5xx.html,内容如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"></meta>
<title>5xx</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>对不起,系统出错了!</h2>
<p th:text="'timestamp : ' + ${timestamp}"></p>
<p th:text="'status : ' + ${status}"></p>
<p th:text="'error : ' + ${error}"></p>
<p th:text="'message : ' + ${message}"></p>
<p th:text="'path : ' + ${path}"></p>
<p></p>
</body>
</html>2、测试
修改上边的HomeController,添加方法:
@GetMapping("/err")
@ResponseBody
public ResultMsg error() throws Exception {
throw new Exception("错误信息");
}启动应用,访问http://localhost:8080/err,可以看到已经成功显示5xx.html,并且输出了正确的信息。
Spring Boot还提供了更加精确的控制自定义页面的方式,这里不再详述。
示例源码见 Github。